This guide explains how to apply effective server hardening techniques across different hosting environments. Learn the core practices, configurations, and tools used to secure servers against attacks, maintain uptime, and protect sensitive data. From firewalls and SSH policies to WordPress and control panel hardening, it outlines a practical framework for building and maintaining safer, more reliable infrastructure.
When you build online, your server is your foundation. Everything depends on how secure that foundation is, your performance, reliability, and customer trust.
According to Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report, over 70% of breaches in hosting environments stem from misconfigurations or unpatched systems, issues that strong server hardening directly prevents.
That’s where server hardening comes in. Think of it as locking all the doors and windows in a building, then removing the doors you don’t actually need.
Server hardening isn’t a one-time checklist. It’s an ongoing practice built into every layer of your infrastructure. You’ll see it in how firewalls are set up, how login access is controlled, and how systems are monitored for threats around the clock.
This guide explains what server hardening means, how to apply it at every level, and how to protect your hosting environment using proven methods.
Understanding Server Hardening
Server hardening means reducing vulnerabilities, the weak points attackers could use to break in. You do this by locking down services, permissions, and configurations.
The goal is simple: minimize the number of ways someone could access your system without permission.
A hardened server runs fewer processes (background programs), enforces stronger authentication (login requirements), and maintains continuous monitoring. It’s not about building an impenetrable wall. It’s about managing risk, keeping systems current, and reacting quickly when new threats emerge.
Effective server hardening requires thinking about servers in a specific way. They need to be optimized not just for speed, but for the ability to withstand attacks. Every update, policy, and patch should protect your speed, stability, and uptime.

Why Server Hardening Matters for Your Hosting Environment
When you invest in web hosting, you’re not just renting server space. You’re trusting that environment to store data, handle traffic, and run applications safely. Server hardening ensures your infrastructure stays scalable infrastructure that grows with your business.
Here’s what it delivers:
Fewer vulnerabilities: Closing open ports (entry points to your server) and disabling unused services reduces your attack surface, the total area where an attacker might get in.
Stronger uptime: Firewalls (built-in security layers), intrusion detection (alarm systems), and access controls prevent downtime from malicious activity.
Compliance readiness: Many industries require hardened environments to meet standards like PCI DSS (payment card security) or GDPR (data privacy).
Better performance: A lean, well-configured server runs faster and uses fewer resources. When you remove unnecessary processes, there’s more computing power available for what matters.
Trust and confidence: Your clients and visitors know their data is safe.
For organizations from solo founders to enterprise teams, proper hardening eliminates hidden vulnerabilities and creates a foundation for sustainable growth.
A Comprehensive Approach to Server Hardening
Enterprise-grade server hardening must be applied at every layer of infrastructure. The principle is “secure by default”, every server starts from a hardened baseline before you add anything to it. To learn more about baselines, check out this Reddit thread or CIS’ benchmarks list.
Here are security measures that should be implemented across various types of hosting.
1. Shared Hosting: Secure Foundations for Every Account
Built-In Account Protection
In shared hosting, multiple users share the same physical server, so isolation is the foundation of security. Make sure each account operates within its own protected environment, separated from every other user. This ensures that files, databases, and resources remain private and stable, even when many sites run on the same machine.
Automated Threat Detection
Security tools constantly monitor for suspicious activity in the background. We recommend using Web Application Firewalls like ModSecurity block common attacks, while malware scanners such as Monarx and ClamAV detect and quarantine infected files. MailChannels filters harmful emails before they can affect performance or deliver malicious code. Together, these automated systems keep threats contained without manual oversight.
Data Encryption and Safe Connections
To protect visitor interactions, make sure that every shared account includes SSL certificates and enforced HTTPS. This encrypts sensitive information (logins, form entries, and payment data) as it travels between browser and server. It’s a layer of hardening that’s visible to your users and silent in operation.
2. VPS Hosting: Full Control with Managed Protection
Access and Account Security
When you move to a Virtual Private Server (VPS), you get your own isolated environment. However, full administrative control also means full responsibility for security. SSH access should use key-based authentication instead of passwords to reduce the risk of brute-force attacks. Privileged actions are limited to specific administrative users, while root logins are disabled by default. Changing the default SSH port and applying strict permission rules further narrow the attack surface.

Active Threat Monitoring and Prevention
Modern VPS platforms include built-in firewall and intrusion detection systems to handle network protection automatically. ConfigServer Firewall and Advanced Policy Firewall manage rules for open ports and monitor for unusual activity. Login protection tools like cPHulk or Fail2Ban detect repeated login failures and block suspicious IP addresses. Malware scanners such as ClamAV and Maldet continuously inspect files to identify and isolate potential threats.
Data Integrity and Performance Assurance
Keeping server software current is a core part of hardening. Regular kernel patches, operating system updates, and PHP version maintenance help prevent vulnerabilities caused by outdated code. Automated backup systems follow the 3-2-1 rule (three copies, two media types, one offsite) ensuring data recovery if an incident occurs. These steps help maintain both security and consistent performance as the server scales.
3. Dedicated Hosting: Hardened Performance at Scale
A dedicated server provides full control over a physical machine, giving you the flexibility to configure hardware, software, and security settings as needed. That freedom also makes you responsible for maintaining every layer of protection.
Start with a Hardened Base
Security begins with a minimal operating system installation that includes only essential components. Reducing unnecessary services and packages limits potential vulnerabilities and improves overall performance.
Establish Strong Network and System Defenses
Once the foundation is set, focus on managing traffic and identifying threats. Firewalls such as ConfigServer Firewall (CSF) regulate network connections, blocking suspicious activity before it reaches critical systems. Complementing the firewall, tools like ClamAV handle virus scanning, rootkit detection, and file monitoring to uncover and isolate malicious code early.
Adapt Security to Each Workload
Hardening measures differ depending on what the server runs. An eCommerce platform may emphasize encryption and intrusion detection, while a content-driven site focuses more on file integrity and controlled user access. Custom policies define these priorities and keep risk in proportion to your actual use case.
Maintain Through Regular Audits
Security isn’t static. Routine updates and kernel patches address new vulnerabilities, while periodic hardening audits confirm that password rules, firewalls, and log management remain aligned with best practices. This steady maintenance cycle ensures the server stays secure and efficient over time.
4. WordPress Hosting: Built-in Hardening with Security Tools
WordPress powers over 40% of websites, which makes it a major target for attackers. WordPress hosting needs both server-level and application-level protection.

This is important in WordPress, as 7,966 new vulnerabilities were found in the WordPress ecosystem in 2024 alone. Comprehensive security plugins like WP Cerber Security can replace multiple single-purpose plugins, simplifying your setup.
Application Hardening in WordPress
Modern WordPress security tools include centralized dashboards that let you enable multiple protection layers without touching code. Within these interfaces, you can:
Prevent unauthorized user discovery by blocking username lookups through author pages or API queries.
Protect administrative scripts so attackers can’t directly access core WordPress files.
Disable PHP execution in uploads, stopping malicious code disguised as images.
Hide system error messages to avoid revealing information about your setup.
Disable XML-RPC, an outdated feature often used in brute-force attacks.
Restrict REST API access to approved functions or roles, reducing exposure through plugin and theme integrations.
Each of these settings reduces the attack surface at the application level, ensuring that common exploits are neutralized before they can target your files or login system.
Server-Level Safeguards
Below the application layer, server-side hardening provides a second level of protection. Running the latest PHP versions improves both performance and security. Hotlink protection prevents other websites from stealing your bandwidth by embedding your media directly. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) filter harmful requests before they reach your site, while automated backups ensure recovery options if anything goes wrong.
Together, these layers create a balanced environment where WordPress sites remain fast, stable, and resilient against common attack patterns.
5. Control Web Panel (CWP): Powerful Security for Advanced Users
Control Web Panel (CWP) offers a flexible, cost-effective option for businesses that want full control over their hosting environment. It provides a visual interface for managing complex server tasks.
CWP includes essential hardening tools in the dashboard:
Login security controls limit failed login attempts and strengthen user authentication.
AutoSSL integration makes it easy to manage SSL certificates for encrypted connections.
Process limits and SSH toggles control what users can do and how they can access the system.
Backup scheduling for both local and remote storage.
While CWP doesn’t include two-factor authentication (requiring two forms of identification to log in) by default, it supports plugins to add this and other security features:
Maldet and ClamAV for malware detection
Rkhunter for rootkit scanning
ConfigServer Firewall (CSF) for port and IP control
Lynis for full system audits
ModSecurity for web traffic filtering
PHP Defender with Snuffleupagus for advanced PHP hardening
The key to securing CWP is keeping it updated and regularly reviewing your log files for unusual activity. Support teams should help ensure your control panel follows the latest best practices.
How Server Hardening Improves Performance
Security and performance aren’t competing priorities. They actually strengthen each other.
Here’s why: When you disable unused services, limit open ports, and optimize authentication, your server runs more efficiently. Every background process you remove frees up CPU cycles and memory.
Think of it like cleaning out a cluttered room. With less clutter, you can move faster and find what you need more easily.
NVMe-based infrastructure (extremely fast solid-state storage) takes this further. Hardened systems generate cleaner, more predictable workloads. This allows NVMe storage to deliver faster response times with consistent latency.
This is how modern hosting achieves 99.9%+ uptime SLAs, by engineering for speed and security as a unified goal, not separate departments.
Common Server Hardening Mistakes (and How to Avoid Them)
Even experienced administrators can overlook critical details. Here are common pitfalls and how to prevent them:
Leaving FTP enabled: FTP (File Transfer Protocol) sends data unencrypted, including passwords. Always use SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) instead. Disable FTP entirely through your control panel.
Keeping root logins active: Root is the most powerful account with unlimited access. Create a separate admin user for daily tasks and disable root logins in your SSH configuration.
Neglecting backups: A backup you haven’t tested isn’t reliable. Schedule regular restore tests to verify your backups actually work.
Ignoring software updates: Outdated CMS plugins and OS packages are common attack vectors, known vulnerabilities that attackers actively exploit. Automate updates whenever possible.
Weak password policies: Enforce minimum length, complexity requirements, and regular password changes across all accounts.
Skipping firewall audits: Even one unnecessary open port creates exposure. Review your firewall rules regularly.
Exposing PHP errors publicly: Error messages can reveal information about your server configuration. Disable public error display and log errors privately instead.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures your hardening efforts actually protect your systems instead of leaving hidden gaps.
When to Rely On Managed Hosting
Server hardening requires constant attention. Threats evolve daily, software changes frequently, and new vulnerabilities appear without warning.
This is why many businesses choose managed hosting solutions. The value isn’t just technical, it’s about time and expertise.
Managed services typically include:
24/7 monitoring and support from real people
Automatic security updates and patching
Regular hardening audits
Backup verification and restore assistance
Expert guidance on compliance and configuration
Organizations can manage these tasks internally if they have dedicated security staff. However, for businesses that want to focus on growth while maintaining strong security, managed hosting ensures systems stay hardened without interrupting daily operations.
The question isn’t about capability, it’s about where you want to invest your team’s time and attention.
The Continuous Cycle of Hardening
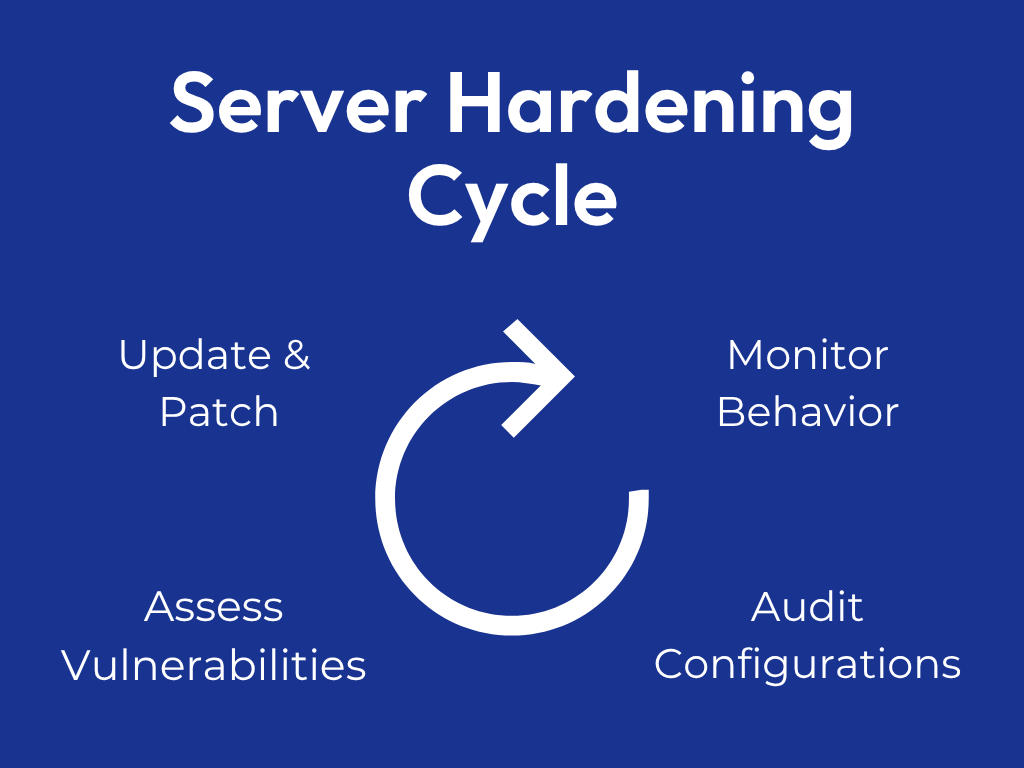
Server hardening isn’t a project with an end date. It’s an ongoing cycle that never stops.
Effective security teams follow this continuous process:
Assessing vulnerabilities through regular log reviews and security scans. What worked last month might not be enough this month.
Updating and patching servers and applications as soon as fixes become available. Delays create windows of opportunity for attackers.
Monitoring behavior for unusual patterns that might indicate a breach or attack in progress.
Auditing configurations to catch drift over time. Systems gradually change as people make adjustments. Regular audits ensure you haven’t accidentally weakened your security.
When applied consistently, this cycle keeps your infrastructure resilient, responsive, and ready for growth.
Summary
Server hardening is the foundation of secure, performance-first hosting. It combines system-level configurations, application-layer protections, and ongoing operational oversight.
Modern hosting providers should integrate hardening into every product and service layer from comprehensive VPS frameworks to WordPress security tools and control panel protections.
The methods described here aren’t theoretical. They’re proven practices used by organizations from startups to enterprises.
With these layers in place, you can focus on building your business. Your servers are hardened, monitored, and supported by teams who treat security as a core operational principle, not an afterthought.
The goal is simple: protect your foundation so everything built on top of it can thrive.
Ready to harden your infrastructure the performance-first way?
Partner with InMotion Hosting, the hosting provider behind ambitious brands, built for speed, security, and scalability.

